3D Scanning Technology in Business
In this Blog article, Reverse Engineering Service expert Mako GmbH discusses how 3D Scanning is being used by Businesses today in today’s world. 3D scanning is a very helpful tool in the quality control stage of any kind of manufacturing and other important business areas.
How 3D Scanning is being used in manufacturing today and the benefits of the technology?
A common use of 3D scanning in the manufacturing process is to check the quality of the goods being produced. This is how many industries offering design, pattern making, heat-treating and machining, is utilizing 3D scanning. Many uses an EinScan H, HX, Pro or Pro HD handheld scanner to measure and check the castings it produces, which can weigh up to 30,000 pounds. Once created, a casting is digitized and compared to its original CAD file. This has proved a very quick way to make sure that castings are meeting specifications. Many Industries claims that historically casting jobs could take 10 days to produce, however, by using a handheld scanner that time has been decreased to six to 10 hours. Additionally, it has also helped the company’s production methods, for example, the technology has been used to find errors in areas of castings that can be traced back to uneven cooling.
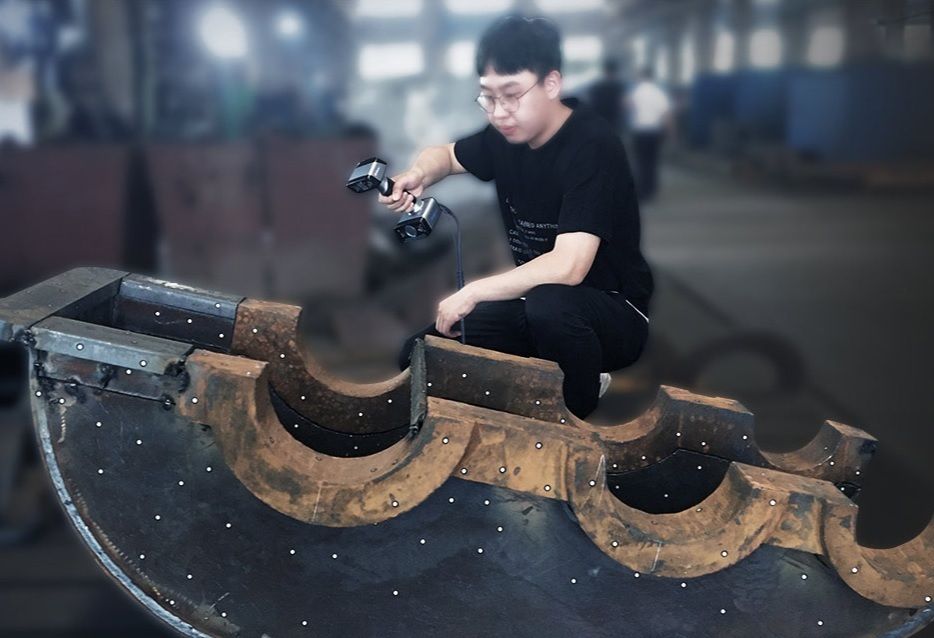

If you are interested in purchasing a 3D Scanner suitable for your business, check out our website dedicated to provide you high quality 3D scanners with latest technology.
3D scanning is a useful tool in the quality control stage of any kind of manufacturing. This is especially true when you are dealing with large products, such as ships or planes. Due to their size, quite significant errors build up when all the parts are put together, varying by several meters, and so the only effective way of finding out the size and shape of the final product is to 3D scan it.
Quality Control
It’s not only the quality of the final product that can be verified by 3D scanning, but also the supplies of parts that go into the product, not to mention the condition of the manufacturing equipment itself – molds, ceramic insulation of furnaces, to name a few.

How do we see 3D technology developing in the future as it relates to the manufacturing industry?
Additive manufacturing is the future. At the moment, it is only small parts that are being made in this way, but in the future, it will be large parts too. Eventually, 3D scanners and 3D printers are likely to become one solution, similar to how 2D scanners have now been integrated into 2D printers. Additive manufacturing will be much faster and much cheaper than molding. Plus, it will allow for the manufacturing of objects that traditional manufacturing can’t produce, such as a ball inside a ball.
What other industries will be most impacted by 3D scanning outside of manufacturing?
3D scanning is used by a diverse array of industries including historical preservation, special effects for movies and video games, healthcare, art and design, and more. One particularly interesting area that is developing is virtual and augmented reality. This could be for entertainment, for businesses that want to create virtual show rooms and even training applications. At the moment, applications such as training are only used in the most high-tech scenarios.
NASA is one of the early adopters of this strategy, with the creation of their Hybrid Reality Lab. This lab combines consumer VR technology and tracked 3D objects (locating an object in 3D space using object tracking technology) to create an immersive experience through realistic visuals and tactile feedback. After the initial investment into the technology, VR will provide a much cheaper way to provide training for a variety of jobs. This training method is expected to continue to grow in terms of popularity and adoption.
If you want to explore more about 3D scanning, 3D scanners, Reverse Engineering and CAD software, then check out our Blog Posts here or contact us here to get in touch with a Reverse Engineering expert!